Introduction
Cloud and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) are two related solutions leaders consider when evaluating technology options to run their businesses. In the cloud world, they will also see terms such as IaaS, PaaS, cloud computing, private cloud, public cloud, and hybrid cloud.
According to an IDC's March 2020 report, more than 90% of global enterprises will rely on a hybrid cloud by 2022. To select the right technology for your company, it is essential to understand cloud computing terms, as these will affect the infrastructure and processes your company is built on, and determine the way you provide value to your customers.
Let's look at how SaaS and cloud relate to each other.
SaaS vs Cloud
Cloud computing enables a user to customize and manage any software application on a server hosted remotely by a third-party provider, such as Amazon AWS, Google Cloud or Azure. Cloud computing lets you provide access to your data on those servers via the internet.
SaaS is a subset of cloud computing. Besides SaaS, cloud computing offers two other service models, IaaS (infrastructure as a service) and PaaS (platform as a service). Each one covers an aspect of IT management as an alternative to on-premise IT solutions.
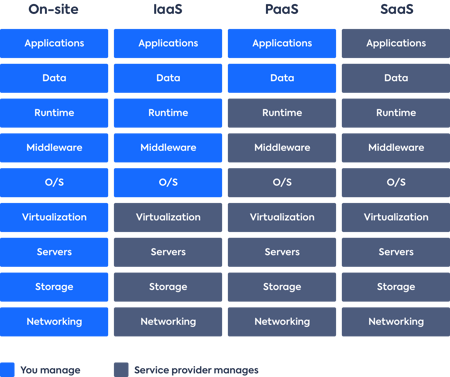
With SaaS, the software is delivered and ready-to-use over the internet. SaaS provides already developed software, through a monthly or annual subscription, without any responsibility to maintain the software. Using SaaS involves losing some control over the application's management and customization which we explain in the IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS comparison guide.
Which is best for your situation? Organizations use IaaS or PaaS if they want to build and customize their own apps to satisfy their needs, and SaaS to solve business processes with out-of-the-box solutions.
To understand each one in more detail, let's go over the short definitions and examples.
What is cloud-based?
Cloud computing describes the use and delivery of hardware and software delivered via the internet. On-demand computing services allow users to access their applications and servers from any device without having to store data on their physical hard drives.
The term “cloud” doesn’t allude to the actual server location, but rather to the idea that users can access information remotely as if it existed in a ubiquitous virtual space. However, since cloud services are delivered through the Internet, users need to be connected to a network in order to use an online application or retrieve data that is stored in an online database.
An organization can have a multi-cloud infrastructure, using more than one cloud platform to achieve its end goals. The three most common deployment models can be split up into the following three groups: private, public, and hybrid cloud.
Some well-known examples of cloud computing (IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS) are Amazon Web Services (AWS), IBM Cloud, Google App Engine, OpenShift, Salesforce, Dropbox, and Slack.
What is a SaaS-based application?
SaaS or Software as Service is the most well-known cloud computing model as it is used on a day-to-day basis not only by large companies but many end-users around the world. It involves the delivery of an application as a service that is ready-to-use and hosted in the cloud.
This computing service is normally available via subscription or a pay-per-use licensing agreement. Accessed through any internet browser, SaaS often increases overall ROI since it doesn’t require any maintenance or updates by the user. With its cost-effectiveness, it has become a vital tool in sales, communications, customer relationships, and project management.
Some well-known examples of SaaS are Salesforce, Zendesk, HubSpot, Dropbox, Slack, and DocuSign.
Business benefits of SaaS and cloud computing
By switching to a cloud-based infrastructure or migrating to SaaS specifically, businesses can move their big computer clusters into cyberspace and thus increase their IT capacity without having to worry about acquiring or maintaining costly in-house servers.
SaaS and cloud-based services offer the following benefits:
Efficiency and cost reduction
There is no need to hire large IT teams since cloud service providers take care of troubleshooting and maintaining their service. Companies also don’t have to spend large amounts of money on purchasing and maintaining technical equipment.
Data security
Cloud storage and software come with advanced protections like encryptions, access control, and layered authentication modules. For additional security, companies can deploy a private cloud model.
Scalability
Companies gain high-performance and fit-to-size solutions at their fingertips without having to invest in or not even using their expensive hardware. Businesses of all sizes can to quickly react to the changing demands of a dynamic marketplace.
Mobility
Access to the cloud is not limited to the corporate office, but rather is freely available virtually wherever it’s needed. By using login credentials, employees can connect to company data, software, and storage servers, complete their tasks from remote locations and always stay in the loop, without performing manual software updates as the systems are maintained automatically.
Disaster Recovery
Cloud computing offers quick and uncomplicated recovery of lost data. With a cloud infrastructure, data is not only available 24/7, but it’s also automatically backed up.
Control
While cloud computing offers customizable solutions for modern businesses, it also lets them have complete control over their sensitive data. With just a few clicks, team leads can adjust access rights and make sure that no information gets into the wrong hands.
Conclusion
With cloud or a subset like SaaS, CIOs can prepare their organizations to succeed in the new digital market. Requiring little to no maintenance, and providing excellent reliability and almost anywhere access, the cloud eliminates the need to install and run applications on individual computers.


