How to perform a technology risk assessment
Now that we have established the benefits, you will probably want to know what the steps are to create a thorough technology risk assessment.
We recommend the following:
1. Get a complete list of applications you use
Hopefully, you have been documenting your applications over the past year. If not, I would suggest first reading our rules and guidelines for Application Rationalization.
Without an overview of your current application landscape, it does not make sense to start a technology assessment. You wouldn’t start baking a cake without a list of ingredients, right? As a first step, you need to collect a list of all the applications you are currently using in your enterprise.
2. Assess the software versions that are in use
The next step is to find out what software versions are being used.
As a best practice, we recommend using a technology stack to group your software. You can also tag your software (manually or using out-of-the-box LeanIX tags) to reference them in the future. In the screenshot example below, you can see that we have tagged them via the Candidate, Leading, Exception, Sunset model.
3. Assess servers and data centers in use
This next step is similar to the previous ones. We recommend again assigning a technology stack to each server and data center.
In this step, you should also verify the data. For example, you can check where your servers are located by using an IT component location report.
4. Link software and servers to applications
After having collected and verified all of the data in the previous steps, it is important to now create the link between software, servers, and applications. This lets you later understand the dependencies between these objects, and thus avoid situations like the one previously described.

Image 4: Free draw report showing dependencies between an application and its IT components and technical stacks.
5. Find out how technology affects your business
You made it to the final step. Now it’s time to find out what technology risk actually means for your business. Time to put the pieces together, for example, we can now use find out where applications using certain software versions are hosted.
End-of-life management
One of the most important factors in technology risk management is obsolescence risk management.
What does this mean? Companies that don’t pay attention to deployed technology reaching obsolescence face a higher number of security risks and vulnerabilities than companies that keep a close eye on the life-cycle of elements in their IT landscape. Also, continuing to use hardware or software that is no longer supported makes it easier for cybercriminals to gain access to systems and data.
This crucial topic is often overlooked, even government agencies are not immune to this. US Government auditors blasted the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in 2015 for missing deadlines to upgrade Windows XP PCs and data center servers running Windows Server 2003, both of which have been retired by Microsoft.
Nine months after Windows XP fell off Microsoft’s support list, the agency still could not account for 1,300 PCs, about 1% of its total, and so could not say whether they had been purged of the ancient OS. The IRS also had to pay Microsoft for post-retirement support contracts to be provided with critical security updates.
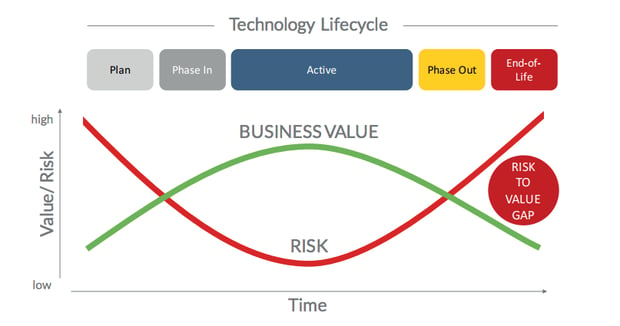
Figure 5 - The business impact of technology obsolescence.
📚 Related: Technology Lifecycle Management
Compliance
Businesses need to comply with many regulations from HIPAA to PCI and FISMA. While compliance does cost money and in terms of technology, requires an accurate view of applications and technology, the cost of non-compliance is usually higher. As a rule of thumb, experts say that the cost of non-compliance is 2.5 times higher than the cost of compliance.
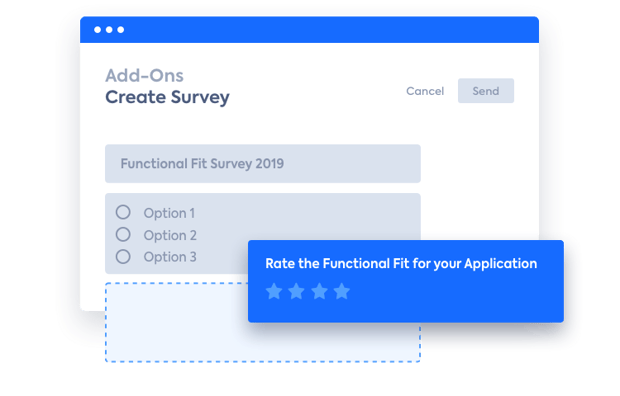
An up-to-date EA Inventory does not only provide you with reliable data that you can use to document your compliance with regulations. The LeanIX Survey Add-on can also help you to create ad-hoc or regular surveys for the appropriate staff to maintain accurate information about, for example, the use of sensitive data by applications.
A current EA use case is GDPR for example; We can assess our data to determine their level of privacy sensitivity, categorizing them as public/unclassified, sensitive, restricted, or confidential. If you are using a professional enterprise architecture management tool such as LeanIX, you can use tags to add further attributes (e.g. "GDPR restricted") to a data object or application. This will usually already be part of your internal security processes, where you assign attributes such as confidentiality, integrity, or availability to data.
![How Application Rationalization Contributes to the Bottom Line - and a Guide to Do it [White Paper]:Learn everything you need to know about application portfolio management (APM), including best practices, how to get started with APM and a complete guide on application portfolio management. »](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/2570476/7208ee2f-46f1-4fa0-a0dd-9a43dbfef8ce.png)
Complexity
Complexity is the enemy of security. When it comes to the retirement of old technology, CIOs have to carefully balance two aspects. On the one hand, they need to “keep the lights on”. They need to make sure, above everything else, that IT operations are running smoothly.
The old proverb says, “If it isn't broken, don’t fix it,” but this adage was not written with digital transformation in mind. There is, of course, some truth in the saying, as an upgrade to newer technology usually is accompanied by some kind of interruption, but keeping the status quo comes at the cost of increased complexity.

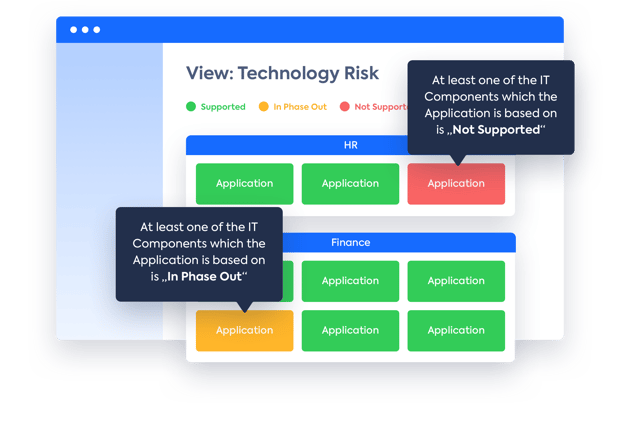
Figure 6: LeanIX dashboard illustrates which applications are at risk as the underlying IT components are out of the lifecycle.
Obsolescence and hardware maintenance, as well as security, are some of the most pressing information technology problems facing organizations today. Not planning for the future of technology is by far one of the most costly IT mistakes that many enterprises make.
Conclusion
Most companies are much better at introducing new technologies than retiring them. The cost of running unsupported technology can be high. Costs of IT outages and data breaches run into the millions.
Technology risk management is a broad, complex topic that cannot be solved by manual data maintenance – no matter how great your team is. With the help of LeanIX software, enterprise architects can quickly source up-to-date technology product information. This information is essential when assessing the risk of the application landscapes, and to plan, manage or retire technology components in a smart way.

![The Enterprise Architect of Tomorrow [White Paper]: Practical insights on how to become data-driven, agile-minded, and forward thinking. »](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/2570476/49fd1c31-67ad-464a-9aae-3ed5e866a24e.png)


/EN-Tech-Stacks-Poster_Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png?width=260&height=171&name=EN-Tech-Stacks-Poster_Resource_Page_Thumbnail.png)

![How Application Rationalization Contributes to the Bottom Line - and a Guide to Do it [White Paper]:Learn everything you need to know about application portfolio management (APM), including best practices, how to get started with APM and a complete guide on application portfolio management. »](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/2570476/7208ee2f-46f1-4fa0-a0dd-9a43dbfef8ce.png)

